Are you considering stocks and options for your investment portfolio? This article provides a straightforward comparison of these two financial instruments, examining their characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and key factors to help you make an informed investment choice.
Investing in options vs. stocks: Pros, cons, and considerations
Table of Contents
What are stocks?
Stocks represent a form of ownership within a company. Purchasing a stock makes you a shareholder, giving you a potential share in the company’s success and the right to vote on certain corporate matters. This ownership position comes with both benefits and challenges.
Stocks can be considered long-term investments, as their value tends to grow over extended periods. They can be used to gradually build wealth, with potential appreciation and income from dividends.
Pros and cons of stock trading
Investing in stocks can provide significant benefits, such as the potential for high returns and portfolio diversification. Still, it also comes with risks, including market volatility and the possibility of financial loss.
Let’s figure out their advantages and challenges below.
Potential advantages of investing in stocks
Understanding the unique features of stocks can help investors recognize the potential benefits they offer.
So, let’s first consider features of stocks that may be beneficial:
-
Dividend income:
Many stocks provide dividend payments, which can offer an additional income stream for their investors. However, not every company distributes dividends, and those that do might modify their dividend policies based on certain factors.
-
Voting rights:
Shareholders typically possess voting rights tied to their shares, impacting choices like electing board members and certain corporate actions. The actual scope and characteristics of these rights, however, may differ depending on the share class and the company’s governing rules.
-
Potential for long-term capital appreciation:
Stocks offer prospects for long-term capital appreciation. However, it’s important to understand that the stock market is dynamic, and past performance is not indicative of future results, even though there have been historical phases of stock growth.
-
Possibility of holding indefinitely:
Unlike certain investments with predetermined timeframes, stocks offer the advantage of indefinite holding periods, granting investors the flexibility to keep them as long as they choose. However, it’s important to note that events like mergers, acquisitions, or delisting can impact continued ownership of the stock.
Potential disadvantages of investing in stocks
There are certain potentially negative aspects of investing in stocks you need to be aware of. They include:
-
Risk of total loss:
One of the biggest drawbacks of stocks is the potential risk of losing your entire principal if the company goes bankrupt or experiences a significant decline in value.
-
Short-term price volatility:
Stock prices can exhibit volatility in the short term, influenced by factors like economic shifts, market sentiment, and company-specific developments.
-
Lack of control:
While shareholders have voting rights, individual investors often have limited control over a company’s day-to-day operations and strategic decisions.
-
Market timing:
Determining when to buy and sell stocks can be tricky, potentially leading to missed gains or market downturns.
What are options?
Options are financial instruments that grant owners the right, but not the obligation, to either purchase (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset like stocks at a predetermined price before a designated expiry.
There are two main types of options:
- Call options: These give you the right to buy a stock at a certain price.
- Put options: These give you the right to sell a stock at a certain price.
Pros and cons of options trading
Investing in options offers the potential for high leverage and flexibility in trading strategies, but it may also carry risks such as complexity, the potential for significant loss, and the need for timely decision-making.
Let’s figure out the pros and cons of investing in options.
Potential advantages of investing in options
Options have several advantages. Let’s delve into some of the commonly acknowledged advantages of options:
-
Flexibility:
Options offer a wide range of strategies, including hedging against market volatility, generating additional income through covered calls, or speculating on price movements through directional plays. Each of the strategies comes with its own risks.
A buyer of the call could lose the premium they paid to purchase the options if not exercised. While a seller (writer) of a covered call forgoes upside stock appreciation above the strike price if assigned. -
Leverage:
Options provide the opportunity to manage a significant position in the underlying asset with a relatively small initial investment. This leverage can possibly increase the potential for both profit and loss if the risks are not carefully managed.
-
Defined risk for option buyers:
For those buying options, the potential loss is limited to the premium paid for the option. This risk limitation provides a predetermined limit on potential losses, offering a structured parameter, not a guarantee, within the uncertainties of volatile markets.
-
Diversification:
Options can be used as a tool for portfolio diversification. By incorporating options strategies with traditional investments, investors may have the opportunity to manage certain risks. It is important to note that diversification alone cannot ensure a profit or protect against loss. It is simply a strategy used to help mitigate risk.
-
Income generation:
Options offer opportunities for generating income, particularly through covered call strategies. Investors can sell call options on stocks they already own, earning premium income while potentially benefiting from stock appreciation up to a certain point. The risk with this strategy is that a writer of covered call forgoes upside stock appreciation above the strike price if assigned. Additionally, key events like an earnings call can significantly impact stock prices, adding another layer of risk for covered call writers during such periods.
Potential challenges of investing in options
Just like stocks, options come with their share of challenges. Here are the main ones:
-
Complexity:
Options come with a steeper learning curve compared to stocks. Understanding the intricacies of options trading, including strategies and pricing models, can be challenging for beginners.
-
Expiration:
Every option has a finite lifespan, leading to a sense of urgency. Your options may expire if you don’t act within the specified time. Managing expiration dates is essential for successful options trading.
-
Market volatility:
Options are highly sensitive to market volatility. Rapid price swings can impact option values significantly, making it essential for investors to monitor and adjust their positions diligently to mitigate unexpected losses.
-
Potential for total loss of premium for option buyers:
While limited risk is an advantage, option buyers face the possibility of losing the entire premium paid if the option doesn’t move in their favor. This contrasts with stockholders who retain ownership even during market downturns.
-
Potentially unlimited risk for option writers:
Option writers, particularly those selling uncovered calls, bear substantial risk. Their potential losses can exceed the premium received, and in some cases, losses can be virtually unlimited if the underlying asset’s price moves significantly against their position.
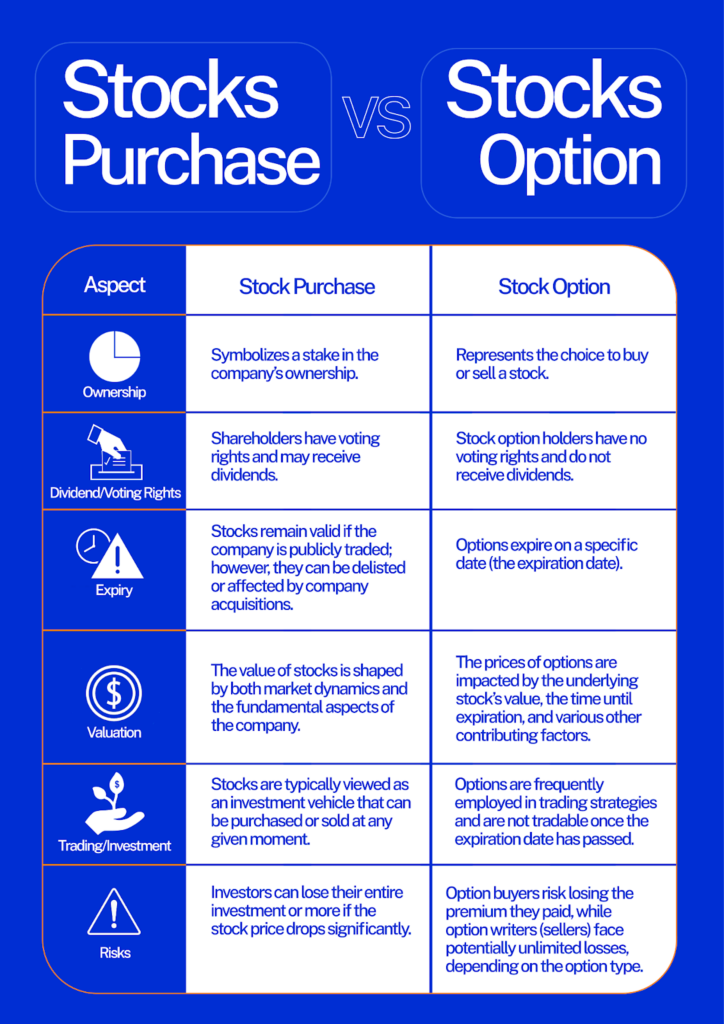
Stock purchase vs. stock option
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences between stock purchases and stock options. Whether you’re considering long-term ownership or exploring options for trading and hedging, this table may help you navigate the choices available in the world of stocks and options.
Making the decision: Options vs. stocks
Deciding between investing in stocks or options depends on multiple factors that must align with your financial circumstances and investment objectives. Here are the key considerations to keep in mind while evaluating which path to choose.
-
Investment goals:
Consider your investment horizon. If you’re looking for long-term wealth accumulation and the potential for dividends, stocks may be the better choice. They offer the opportunity for capital appreciation over time. If you’re seeking short-term gains or hedging strategies, on the other hand, options can provide more flexibility due to their limited timeframes.
-
Risk tolerance and appetite:
Assess your willingness and capacity to withstand market fluctuations. Stocks typically involve less risk for the investor, with losses limited to the invested capital. Options, especially when used for speculative purposes, can be riskier. Options writers, in particular, face unlimited risk. Ensure your choice aligns with your risk appetite.
-
Amount of capital available:
Your available capital is a significant factor. Stocks typically demand a higher initial investment when compared to options. Options, with their lower capital requirements, can facilitate easier portfolio diversification. They, however, also come with the potential for greater percentage gains or losses.
-
Understanding and comfort with complex financial instruments:
Options are sophisticated financial tools. To trade them effectively, you may need a solid grasp of diverse strategies, including calls, puts, and possibly more advanced approaches like spreads and straddles. For individuals new to investing or those seeking straightforward investments, stocks might be a better fit. However, if you’re willing to invest time in learning and navigating the complexities of options, they can become a strategic asset in your investment portfolio.
-
Desired level of involvement:
While many investors take a passive, long-term approach to stocks, there are some that prefer active trading. Options, given their time-sensitive nature, can demand more frequent monitoring. Factors like time decay and market volatility affect option values. Thus, if you’re inclined toward active trading, you might find certain options strategies appealing. However, it’s important to remember that both stocks and options can be volatile, and there’s no universal strategy that guarantees investment success.
-
Knowledge level:
Investors new to the market may find stocks easier to understand and manage. Options require a more market knowledge and active management, especially when dealing with complex strategies like writing options or executing spreads.
-
Time horizon:
Stocks can be more suited for long-term investors looking to build wealth steadily over time. Options, on the other hand, may often be used for short-term strategies due to their expiration dates and time-sensitive nature.
Investing in stocks and options both offer unique opportunities and challenges. Your choice should align with your financial objectives, risk tolerance, and level of engagement. With a solid grasp of these aspects, you can confidently set out on your investment journey.
Finding the right fit: Stocks or options with Public
When it comes to choosing between investing in options or stocks, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. Each has its own set of benefits and risks, making the decision highly dependent on your individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment strategy. Stocks may offer the stability and potential for long-term growth, while options may provide flexibility and leverage but with added complexity and risk.
Ultimately, the key is to choose the path that aligns with your financial goals and comfort level. Whether you’re drawn to the simplicity of stock ownership or the strategic nature of options, both can play a valuable role in building a well-rounded investment portfolio.
To learn more and take the first step toward investing, Sign up on the Public App today and join a community of informed investors!

Frequently Asked Questions
Which requires a larger initial investment, stocks or options?
Stocks generally demand a larger initial investment as you’re purchasing ownership in a company. Options, however, provide a more cost-efficient method to gain exposure to a significant position in a stock with less upfront capital.
Why might an investor choose options over stocks?
Investors might opt for options due to their leverage potential (gaining exposure to a substantial position in the underlying asset with a smaller upfront investment), strategy versatility (like hedging or generating income), and the opportunity to speculate without having ownership of the underlying asset.
How can options help in portfolio diversification?
Options can help diversify your portfolio by offering strategies for hedging and speculation. Similarly, Public.com platform supports diversification by allowing users to invest in a variety of asset classes, including stocks, ETFs, US T-bills, cryptocurrencies, and alternative investments.
How do dividends impact stock and option investors?
Dividends affect stock and option investors differently. For stock investors, dividends work by providing direct profit distributions from the company to its shareholders. In contrast, option investors, specifically call option holders, do not receive dividends directly. The anticipation of dividends, however, can influence option prices. As the ex-dividend date approaches, call options on a stock may become expensive, reflecting the expected dividend payment.
Is it possible to convert an option into a stock?
Yes, it’s possible to convert an option into a stock, but it depends on the type of option being considered. When an investor possesses a call option, they possess the right, though not the obligation, to purchase the underlying stock at the strike price before the option reaches its expiration. With a put option, likewise, investors have the right to sell the underlying stock at the strike price. The decision of whether to exercise these rights is contingent upon several market factors and individual strategies.
How do time horizons differ between stock and option investments?
Stocks retain their value as long as the company is publicly listed, but they can be impacted by delisting or corporate takeovers. In contrast, options come with expiration dates, after which they lose their value.
Can you lose more than you invest in options?
While option buyers’ losses are limited to the premium paid, option sellers, especially those dealing with uncovered options, risk unlimited losses that could exceed their initial investment, if the market moves against them.
What tools may help in effectively trading options?
Specialized tools for market analysis, risk assessment, and real-time monitoring may help. These include options calculators, volatility indicators, and trading platforms with advanced order types.